Email marketing remains one of the most reliable and cost-effective digital marketing strategies available. With a median ROI of 4200%, it continues to outperform many other channels when properly executed.
Yet, the effectiveness of email campaigns hinges on more than just crafting catchy subject lines or sending weekly newsletters.
Success in email marketing demands strategic planning, thoughtful segmentation, ongoing performance analysis, and full compliance with privacy regulations. It involves influencing action, nurturing relationships, and driving measurable business outcomes.
This guide will examine the components of high-performing email campaigns. It will offer insight into how to build and sustain an approach that aligns with both short-term objectives and long-term customer lifecycle management.
From foundational concepts to real-world execution strategies, each section is designed to provide you with clarity on how to elevate your email marketing to a professional standard.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Fundamentals of Email Marketing
To use email marketing effectively, it’s essential to understand its fundamental role in the marketing funnel.
At its core, email marketing is a form of direct communication aimed at engaging leads, converting customers, and strengthening loyalty, all through permission-based outreach.
It is both scalable and personalizable, making it uniquely suited for tailored messaging that fits various stages of the buyer journey.
When paired with analytics and automation, emails evolve into a performance-driven customer engagement engine.
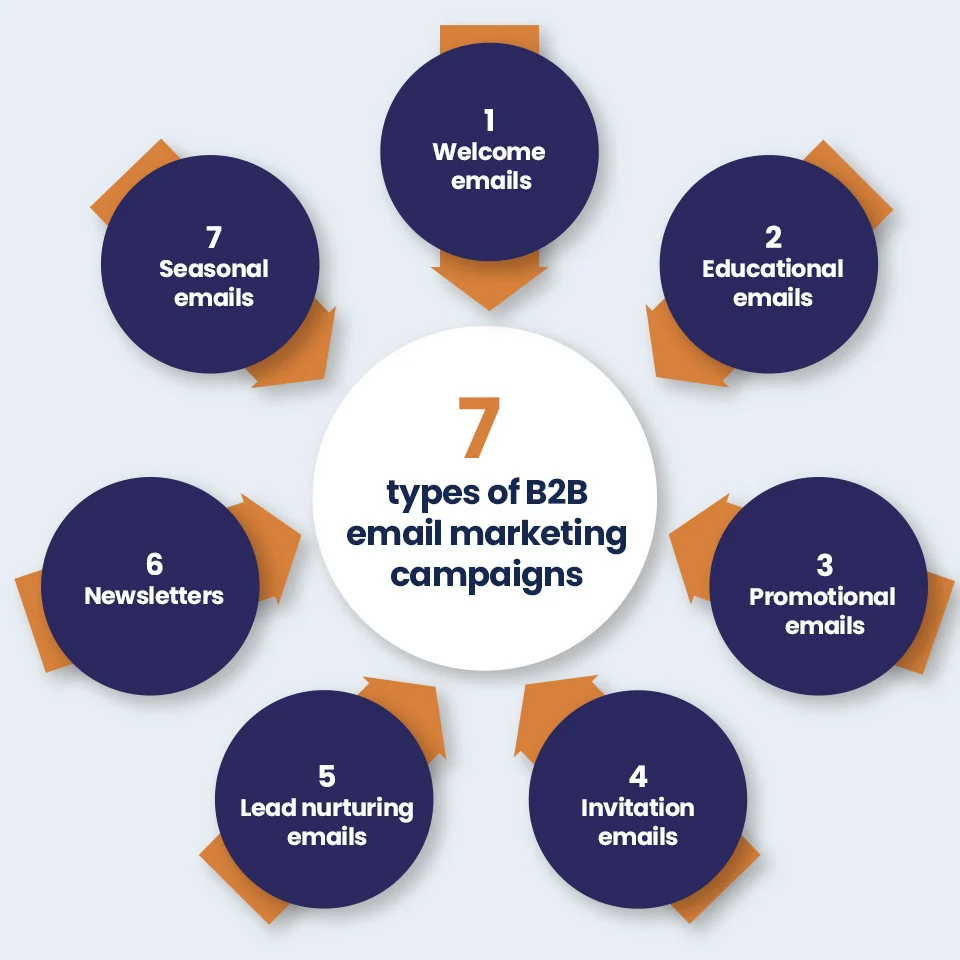
Types of email campaigns include (but are not limited to):
- Newsletters: Recurring emails that share news, updates, or content.
- Promotional Emails: Offers, discounts, or product launches designed to drive conversions.
- Transactional Emails: Order confirmations, shipping updates, and invoices.
- Drip Campaigns: Pre-scheduled sequences triggered by user behavior or milestones.
- Re-Engagement Emails: Efforts to win back dormant subscribers.
- Event Invitations: Webinars, launches, or live events requiring RSVP.
- Survey/Feedback Emails: Used to gather customer insights and satisfaction data.
Meanwhile, there are differences between email marketing in B2B and B2C contexts. Using these different trails can help refine targeting and tone. The table below outlines key distinctions:
| Element | B2B Email Marketing | B2C Email Marketing |
| Decision-making process | Longer, involves multiple stakeholders | Faster, usually individual decisions |
| Content style | Professional, value-driven, solution-focused | Emotional, benefit-driven, concise |
| Frequency | Weekly or bi-weekly | Daily to weekly |
| Metrics of success | Lead quality, meeting bookings | Sales volume, CTR, repeat purchases |
| Call-to-action | Download whitepapers, schedule demos | Shop now, use a discount, read more |
Building a High-Quality Email List
No amount of excellent content or design can compensate for a low-quality list. A healthy email database starts with ethical, organic list-building strategies and evolves through proper segmentation and hygiene practices.
Organic list-building tactics are superior to purchased lists, which often contain unengaged or irrelevant recipients. Begin by integrating sign-up forms across your website: on blog pages, landing pages, and at checkout points. Incorporate double opt-in processes to ensure consent and filter out low-intent signups.
Organic vs Non Organic Newsletter Subscribers
Lead magnets and gated content offer value in exchange for contact information. Examples include downloadable ebooks, access to webinars, exclusive discount codes, or industry reports.
The goal is to attract users who are both interested and likely to convert. Ensuring that the content matches your customer journey stages enhances both list quality and conversion potential.
List hygiene and segmentation are ongoing requirements. Regularly clean your list to remove bounced, inactive, or unsubscribed addresses. This not only improves deliverability but also prevents your sender reputation from deteriorating.
Segmentation allows for smarter targeting. Start with basic filters like demographics, purchase history, or engagement level. Over time, introduce behavioral triggers (such as abandoned cart emails or post-purchase recommendations) to personalize messaging further.
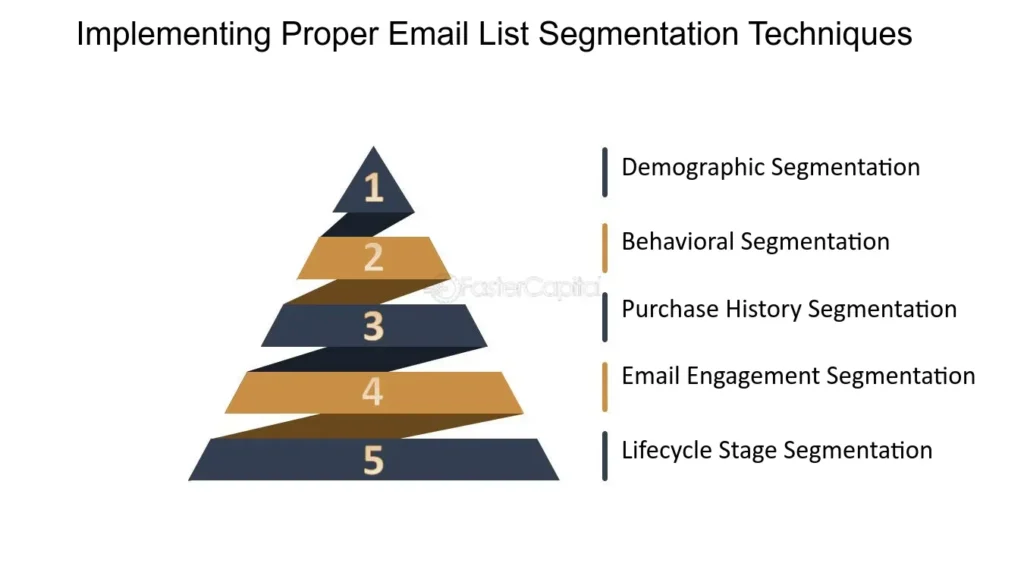
Source: FasterCapital
Ultimately, list quality is less about quantity and more about relevance. A smaller, highly engaged list often yields better results than a bloated list full of passive recipients. Prioritize transparency, relevance, and consistent optimization, and the return on effort will follow.
Crafting a Compelling Email Strategy
An effective email marketing strategy involves aligning every aspect (from goal setting to automation workflows) with business objectives and audience behavior. Without this alignment, even high-quality emails risk underperforming.
Setting Campaign Goals
Defining your campaign goals is foundational. These goals dictate the tone, structure, and metrics for success. Each campaign should serve a single primary aim to avoid message dilution or misaligned calls to action.
- Brand Awareness: Focus on newsletters or welcome sequences. KPIs include open rates and subscriber growth.
- Customer Engagement: Use educational series or event invitations. Engagement is measured via click-through rates and time spent on linked content.
- Conversions: Drive purchases, bookings, or sign-ups. Metrics include conversion rates, ROI, and cart recovery performance.
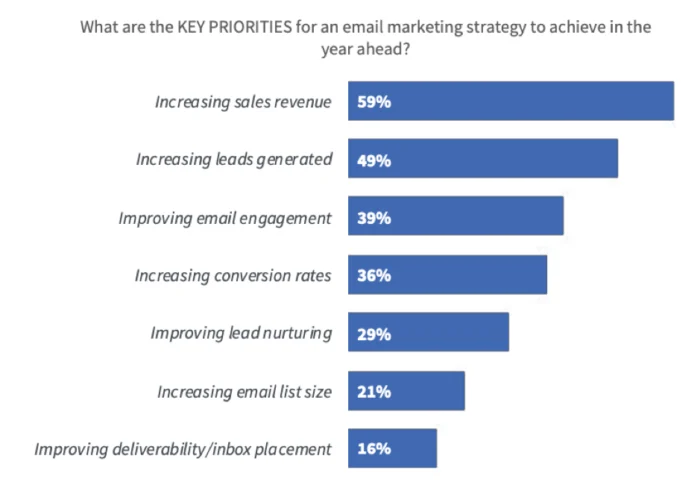
Source: Smart Insights
Frequency, Timing, and Sequence Planning
Over-emailing increases opt-outs; under-emailing reduces impact. The right cadence depends on campaign type, industry norms, and subscriber expectations.
Sequence planning can let emails build logically from awareness to action over time, rather than operating as isolated messages.
Weekly or bi-weekly is standard for B2B educational content. For B2C promotions, 2–3 times a week may be viable if value is delivered consistently.
Testing send times (weekday mornings vs. weekends) often reveals audience preferences.
Automation Workflows and Drip Campaigns
Automation enables scalable personalization and behavior-based targeting. Drip campaigns are particularly valuable for nurturing leads and onboarding customers.
A lead magnet download can trigger a 5-part email series with educational value. Meanwhile, abandoned cart emails can be sequenced over 72 hours with increasing urgency.
Not to mention, you can set it so new subscribers receive a welcome sequence before regular updates.
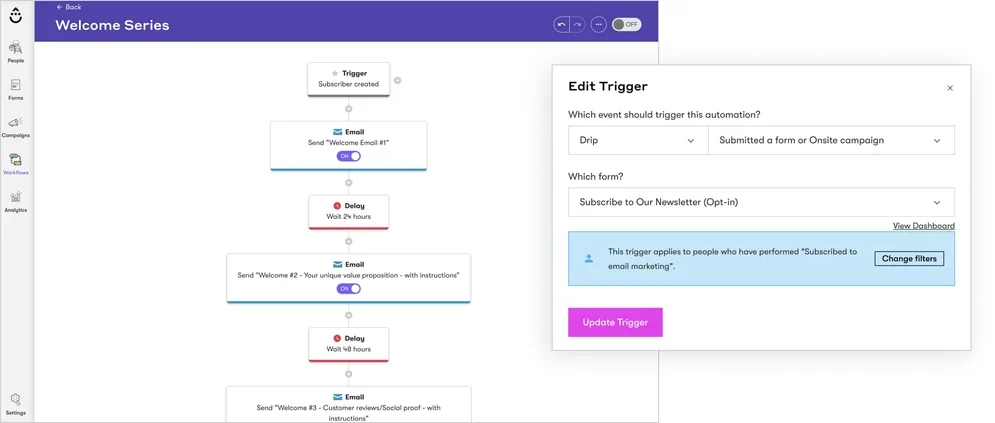
Example: Drip Marketing Automation Workflow
Automation can reduce manual load when workflows are mapped properly while increasing message relevance and timing accuracy.
Design and Content Best Practices
Even the most strategic email campaign can fail if its design and content execution are flawed. Precision in layout, messaging, and structure is critical for optimizing user experience, maintaining attention, and driving action.
The following best practices are grounded in proven performance principles across industries:
- Layout Clarity and Visual Hierarchy: For mobile readability, use single-column formats and highlight the CTA with whitespace, contrasting buttons, and directional cues.
- Responsive Design: Use fluid grids and scalable images to ensure the email displays correctly across devices and major clients. Test emails with tools like Litmus or Email on Acid before sending them.
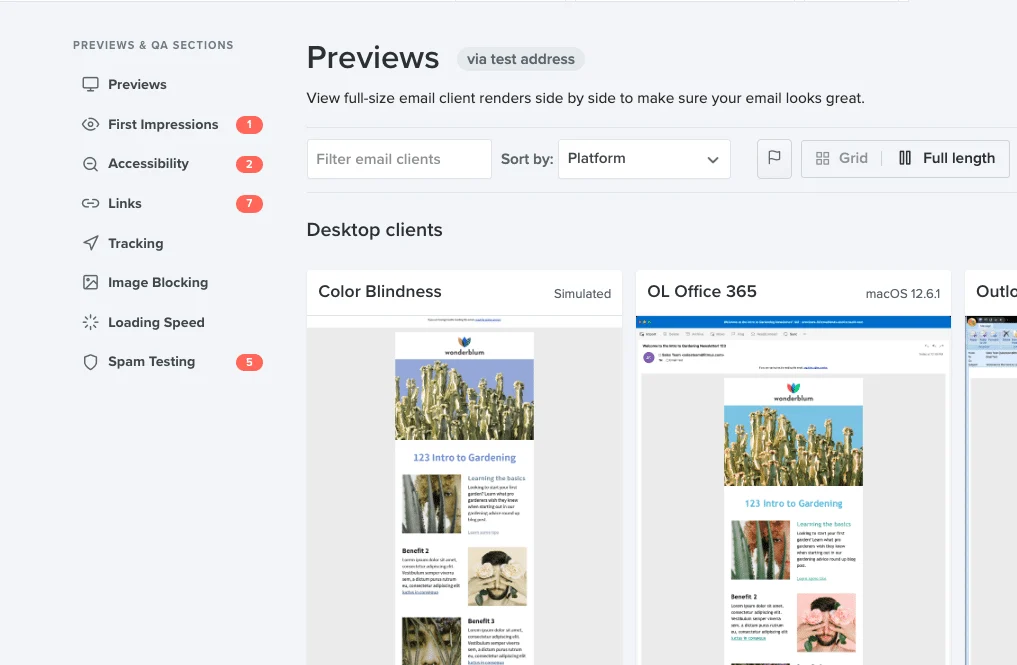
- Concise and Actionable Copy: Structure content into short paragraphs and bullet points. Lead with value in the first sentence and end with a clear, compelling CTA that aligns with your campaign goal.
- Personalization without Overuse: Use dynamic fields for names or preferences where relevant, but avoid excessive insertion of personal data, which may feel intrusive or algorithmic.
- Strategic Image Usage: Keep image sizes optimized for fast loading, include descriptive alt text, and never rely solely on images to convey core messaging or CTAs.
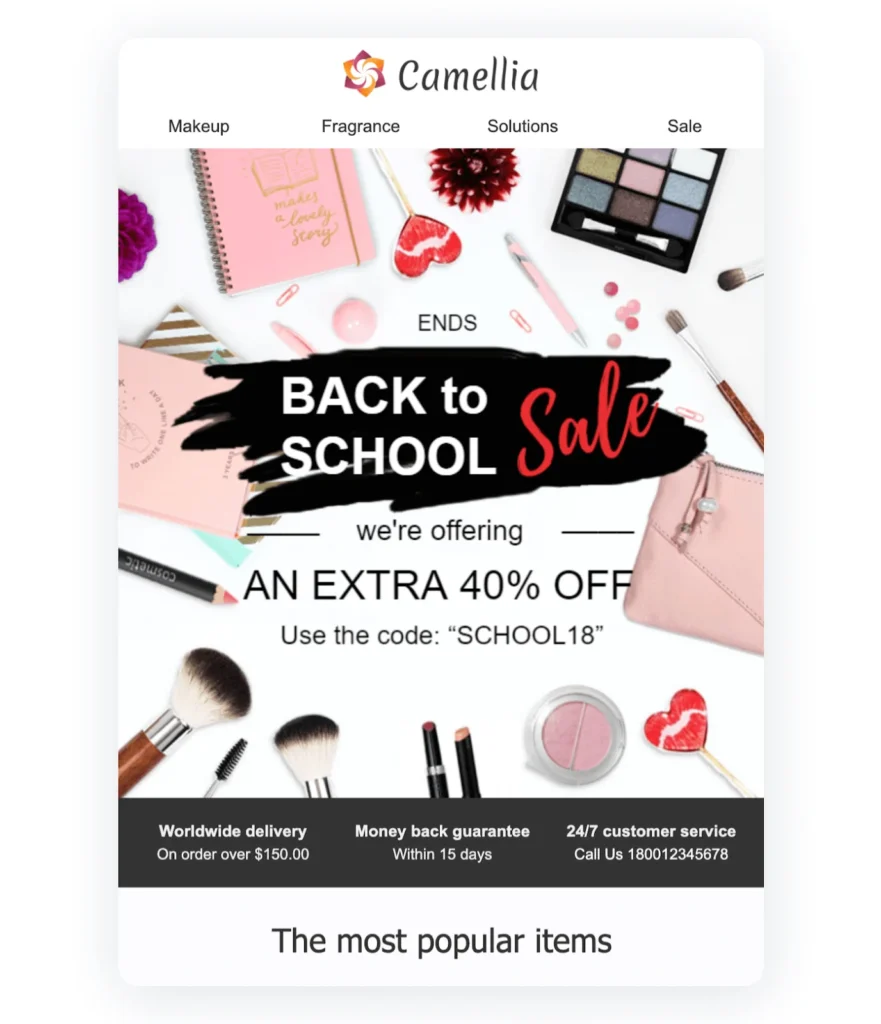
Example: Camellia’s Email Campaign
- Accessibility Considerations: Use high-contrast text and backgrounds, legible font sizes (minimum 14px), and semantic structure. Always provide a plain-text version to support screen readers and improve deliverability.
- CTA Positioning: Place your primary call to action above the fold, repeat it toward the end, and make it visually distinct. Avoid multiple CTAs competing for attention within a single message.
- A/B Testing Framework: Test one element at a time, such as subject lines, CTA phrasing, or hero image selection. Segment your audience to maintain clean data and draw statistically significant conclusions.
Effective email design guides attention, reduces friction, and reinforces the campaign’s intent with every visual and textual element.
A/B Testing and Optimization
Testing is foundational to maximizing campaign efficiency. A/B testing, when done systematically, identifies performance levers and removes guesswork from content and design decisions.
It allows for refined messaging that resonates more accurately with segmented audiences.
Key elements to test include:
- Subject Lines: Try urgency vs. curiosity, short vs. long formats.
- Preheader Text: Support the subject line or add complementary context.
- CTA Wording and Placement: Test actionable vs. benefit-driven language, button color, or in-text vs. graphic buttons.
- Send Times and Days: Analyze variations in open and engagement rates.
- Content Length and Structure: Compare scannable formats to narrative-heavy formats.
- Visual Assets: Swap static images with GIFs or test different header visuals.
Interpreting results requires more than just monitoring uplift in open or click-through rates. Statistical significance matters. Track large enough samples to ensure that the results aren’t coincidental.
Confidence levels of 95% or higher are typically used as a benchmark in professional A/B testing.
More importantly, testing should feed into a continuous improvement loop. Identify insights from each test, apply the learnings to future campaigns, and continue iterating. Over time, this will form a data-informed strategy tailored to audience behavior, not assumptions.
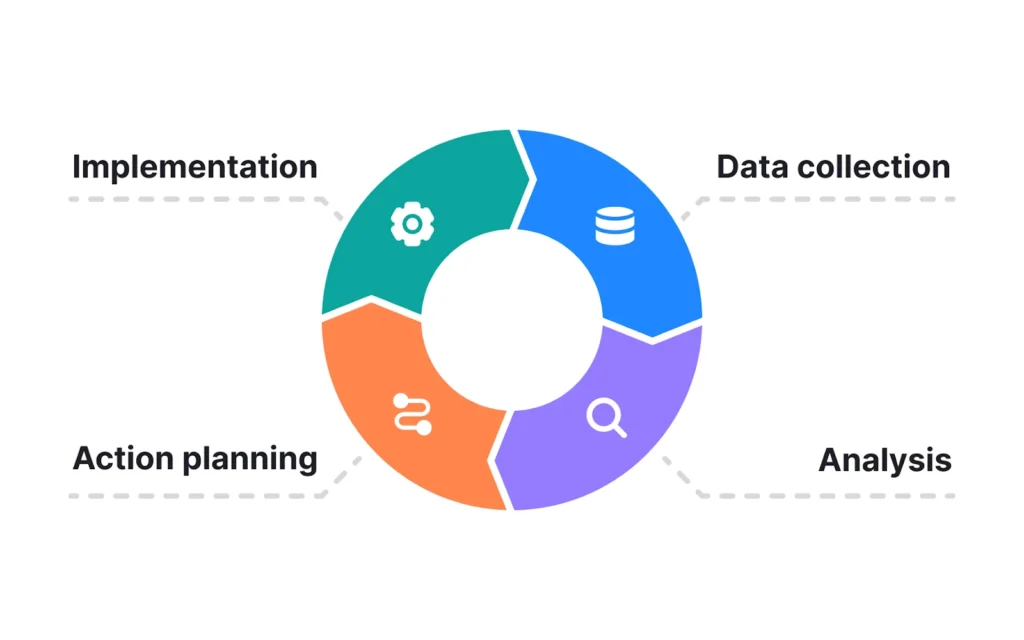
Avoid testing too many variables simultaneously, as this complicates attribution. A disciplined test-design-measure-adjust loop ensures compound gains over time without diluting brand consistency.
Compliance and Deliverability Essentials
Compliance in email marketing is not just legal hygiene; it directly impacts inbox placement and brand integrity. Non-compliance leads to penalties, blacklisting, or severe damage to sender reputation.
The GDPR mandates clear, informed consent before sending emails to EU citizens. It includes transparent privacy notices, easy unsubscribe mechanisms, and proof of opt-in consent.
For U.S. audiences, CAN-SPAM compliance requires truthful subject lines, the physical address of the sender, and opt-out functionality in every message.
Effective opt-in policies include double opt-ins, explicit checkbox agreements, and segmentation based on user preferences. These practices can enhance deliverability and ensure engagement from interested recipients.
To maintain technical deliverability, prioritize the following:
- Monitor Bounce Rates: Identify and remove invalid or outdated addresses promptly.
- Avoid Spam Traps: Regularly clean your list and avoid purchasing email databases.
- Manage Sender Reputation: Authenticate with SPF, DKIM, and DMARC. Maintain consistent sending behavior.
- Use Permission-Based Lists: Only engage users who explicitly opted in.
- Track Feedback Loops: Address user complaints by monitoring ISP complaint rates.
High deliverability results from both legal adherence and technical diligence, and failing at either end will compromise long-term campaign success.
Key Metrics to Track for Success
Tracking the right performance metrics is essential to evaluating the effectiveness of an email campaign. Beyond vanity metrics, each KPI should tie back to the broader business goals of engagement, conversion, and retention.
- Open Rate: Measures how many recipients opened the email. It’s influenced heavily by subject line relevance, sender reputation, and timing. A low open rate indicates poor targeting or uninspiring subject lines.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Reflects the percentage of recipients who clicked on a link in the email. CTR offers insights into content engagement and the strength of the call to action.
- Conversion Rate: Tracks how many recipients took the desired action post-click (e.g., purchase, sign-up, download). It is the clearest indicator of ROI and campaign alignment with audience intent.
- Bounce Rate: Differentiates between hard bounces (invalid addresses) and soft bounces (temporary delivery failures). High bounce rates affect deliverability and sender score.
- Unsubscribe Rate: While inevitable to some degree, high unsubscribe rates suggest misaligned messaging, frequency fatigue, or irrelevance.
- List Growth Rate: Indicates how quickly the email list is growing, factoring in new subscribers and opt-outs. Healthy growth reflects effective acquisition strategies and valuable content.
- Spam Complaint Rate: Measures how often users mark emails as spam. A high rate indicates poor permission practices or overly aggressive messaging.
Collectively, these metrics allow for a granular view of campaign performance and help isolate areas requiring refinement.
Real-World Examples of Successful Campaigns
Successful campaigns are not always about flashy design but often about strategic alignment between message, timing, and audience behavior.
Below are three illustrative examples. These campaigns reflect not just creative execution but disciplined alignment between business objectives and user intent.
Dropbox: Re-engagement Email
Dropbox crafted a re-engagement email targeting inactive users, highlighting the benefits they were missing. The email featured a clean design with a clear call to action, reminding users of the convenience of accessing their files anytime, anywhere.
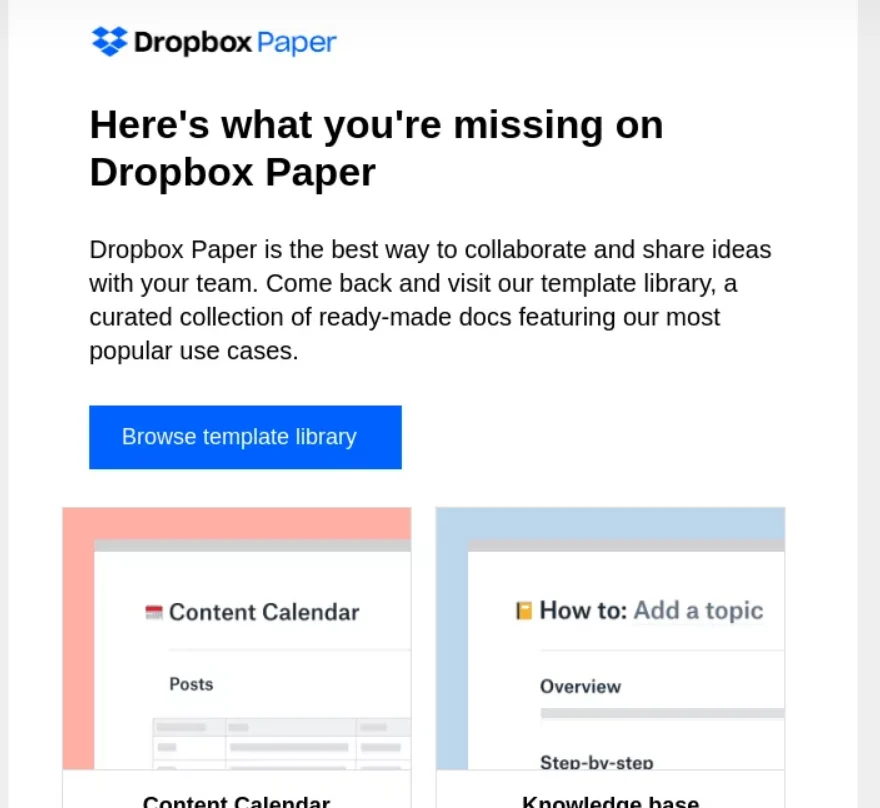
The subject line, “21 reasons to give Dropbox Paper another try,” aimed to rekindle user interest.
BuzzFeed: Personalized Content Newsletter
BuzzFeed’s email campaign utilized personalized content to engage subscribers effectively. By analyzing user behavior and preferences, BuzzFeed sent tailored newsletters featuring articles and quizzes aligned with individual interests.
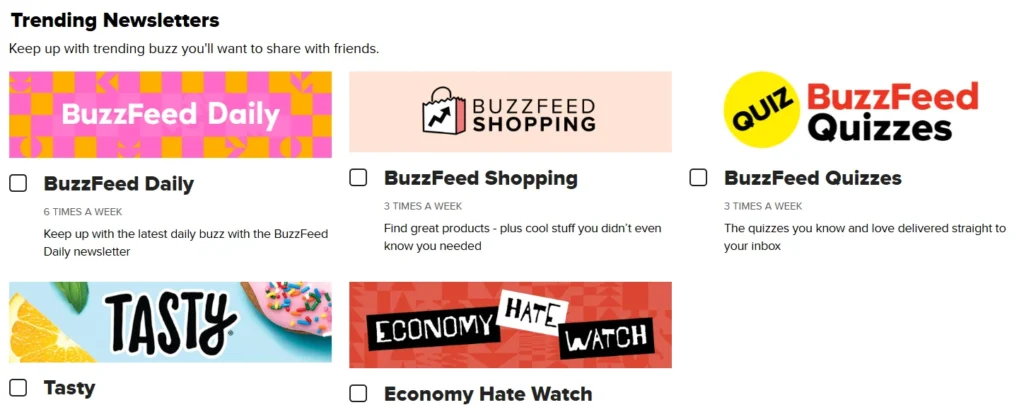
This approach led to higher open and click-through rates, demonstrating the power of personalization in email marketing.
Adobe Creative Cloud: Welcome Series Automation
Adobe implemented an automated welcome series for new Creative Cloud users, introducing them to various features and tools over a sequence of emails. This strategic onboarding process aimed to enhance user engagement and product adoption.
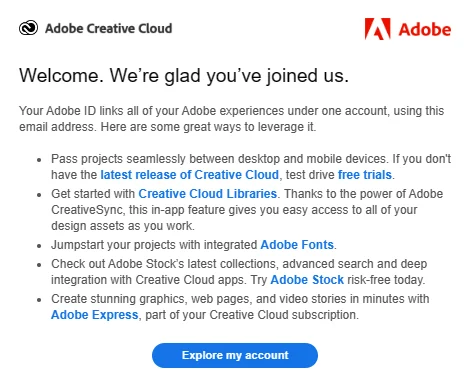
By providing valuable information in a structured manner, Adobe effectively guided users through its offerings.
Integrating Email with Broader Marketing Ecosystems
Email marketing performs best when it operates as a strategic component within a broader, multi-channel marketing framework. Integration enhances consistency, extends reach, and deepens audience engagement across multiple touchpoints.
The alignment of email with content marketing ensures continuity in messaging. For example, blog posts or case studies can be promoted through newsletters, while subscriber behavior can inform future content topics.
Source: WebiBazaar
Similarly, email can support SEO by increasing traffic to key landing pages, aiding their performance in search rankings through user signals and dwell time.
In social media strategies, email lists serve as high-value audiences for retargeting. Businesses can run custom audience campaigns by syncing subscriber data with platforms like Facebook Ads or LinkedIn, driving users from inboxes to social feeds and back. It creates a surround-sound effect across the customer journey.
CRM integration allows for dynamic segmentation and real-time personalization. Behavioral triggers such as product views, cart abandonment, or subscription renewals can prompt timely and relevant email follow-ups.
This tight feedback loop increases responsiveness and conversion potential.
Moreover, marketing automation platforms with omnichannel capabilities (like HubSpot, ActiveCampaign, or Klaviyo) enable workflows where email steps are interwoven with SMS, push notifications, or on-site messages. It maximizes contact frequency without overwhelming the recipient via a single channel.
Treating email as an isolated tactic often leads to stagnation. But when fully integrated, it amplifies the efficiency and effectiveness of the entire marketing ecosystem.
Businesses that execute this alignment well gain superior attribution visibility, stronger customer relationships, and a measurable lift in lifetime value.
Conclusion
Email marketing remains a dynamic and high-impact channel when executed strategically.
For business owners, email remains not just a channel for outreach but a cornerstone of lifecycle marketing. Done right, it can cultivate loyalty, increase conversions, and maximize long-term customer value, far beyond the capabilities of most other digital touchpoints.