Geo-targeting has become one of the most effective tools for driving qualified, local customers directly to physical business locations.
With rising competition in local markets and more consumers searching for nearby services in real time, the ability to reach audiences within specific geographic boundaries is a strategic necessity.
Modern ad platforms now allow for precise segmentation based on location, behavior, and even intent. They enable business owners to focus ad spend where it matters most.
Whether the goal is increasing footfall, promoting limited-time offers, or driving in-store event attendance, geo-targeted campaigns let businesses match messages to hyper-relevant local contexts.
This blog will explore the technical and strategic layers behind geo-targeted advertising. We will explain how the targeting methods work and the platforms and industries that benefit most.
Table of Contents
What Is Geo-Targeting in Digital Advertising?
Geo-targeting in digital advertising refers to the practice of delivering ads to users based on their specific geographic location.
These locations can range from country and city levels to highly focused radii around a physical address. The goal is to ensure ad relevance by matching offers to users’ current or recent locations.
It’s important to distinguish between different location-based targeting methods, as each serves a unique purpose in campaign strategy:
| Type of Targeting | Definition | Use Case Example |
| Geographic Targeting | Targets users by country, region, city, or ZIP code | National retail chains with local branches |
| Radius-Based Targeting | Targets users within a defined distance (e.g., 5 miles) from a specific point | Restaurants targeting nearby mobile users |
| IP-Based Targeting | Uses users’ IP addresses to determine location, typically at the city level | Online services with local offices |
Across major platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and programmatic networks, geo-targeting operates using real-time signals such as GPS, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and IP geolocation.
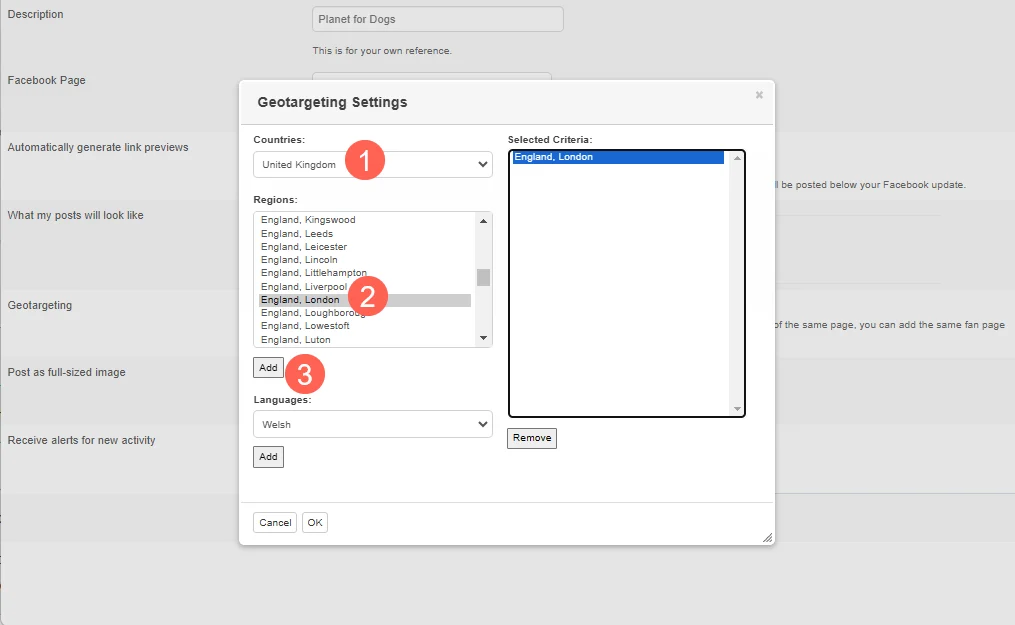
Setting Geotargeting for a Facebook Page
Brick-and-mortar businesses stand to benefit the most. These targeting methods help attract local traffic to physical storefronts, allowing business owners to invest advertising budgets where the potential for offline conversion is highest.
Why Geo-Targeting Is Crucial for Driving Local Foot Traffic
The importance of geo-targeting is directly tied to a fundamental shift in user behavior. More consumers are using mobile devices to find immediate, local solutions to their needs.
This has given rise to local-intent searches such as “coffee shop near me” or “emergency plumber nearby,” which reflect a strong purchase or visit intent.
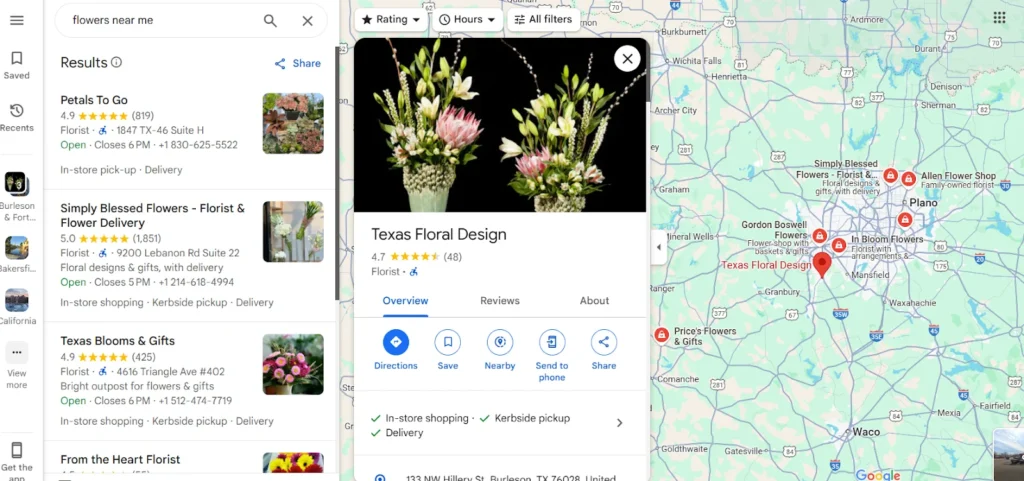
Search engines like Google are increasingly favoring these searches by offering location-aware results at the top of mobile search pages, often supported by local ads.
By leveraging geo-targeting, businesses can position themselves right where potential customers are looking and act on this real-time intent.
The rise in mobile dependency further amplifies this opportunity. Most smartphones constantly share location data, making real-time targeting more accurate and responsive.
Users are also more receptive to localized messaging when on-the-go, increasing the effectiveness of time-sensitive campaigns.
Industries that particularly benefit from geo-targeted advertising include:
- Quick-Service Restaurants – for promoting local lunch specials or flash offers
- Gyms and Fitness Studios – for driving sign-ups or foot traffic within a defined radius
- Auto Service Centers – to target nearby car owners in need of maintenance
- Retail Stores – for in-store promotions, product launches, or seasonal sales
- Healthcare Providers – such as dentists, urgent care, and optometrists, targeting nearby patients.
- Real Estate Agencies – for open houses and local listings visibility
When used effectively, geo-targeting turns location into a performance-driving variable that aligns tightly with users’ behavior and expectations.
Types of Geo-Targeted Ads and How They Work
Geo-targeting spans across multiple advertising formats, each optimized for different user contexts and behaviors. Below are five core types of geo-targeted ads, detailing how each functions and how they can support local foot traffic goals.
Geofencing Ads
Geofencing ads rely on virtual perimeters set around real-world geographic areas. When a user enters the defined boundary with a GPS-enabled device, they become eligible to receive targeted ads, typically via mobile apps or display networks.
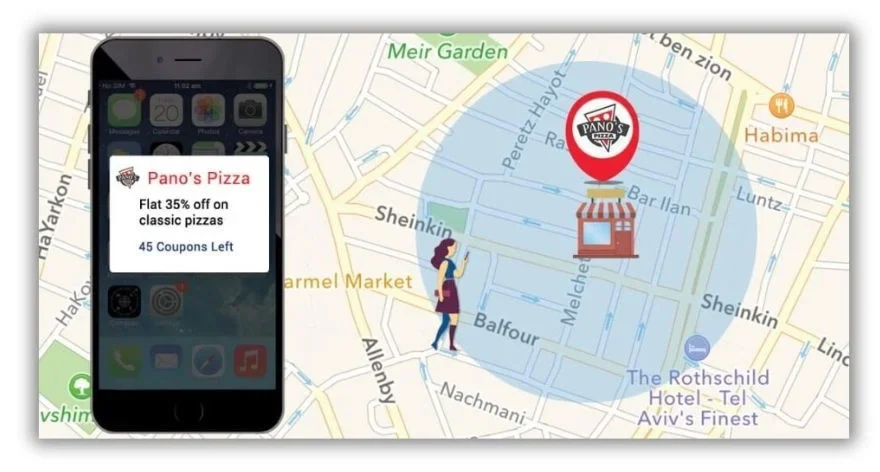
These ads are effective for time-sensitive promotions or events. For example, a retail store might trigger ads for a one-day sale to users who enter a mall complex. Geofencing can also be set around competitor locations to intercept nearby prospects with more compelling offers.
This strategy utilizes real-time location data and often works with mobile ad IDs and push notification systems to reach users during high-intent micro-moments.
Local Search Ads
Local search ads appear when users query keywords with local intent, such as “florist near me” or “open gas station.” These ads are typically served on search engines like Google or Bing and are prioritized based on relevance, proximity, and advertiser bid.
They often include location extensions, click-to-call buttons, and directions links. For instance, a local pizzeria could run ads for “late night pizza” and appear prominently in Google Maps or mobile search results to attract after-hours traffic.
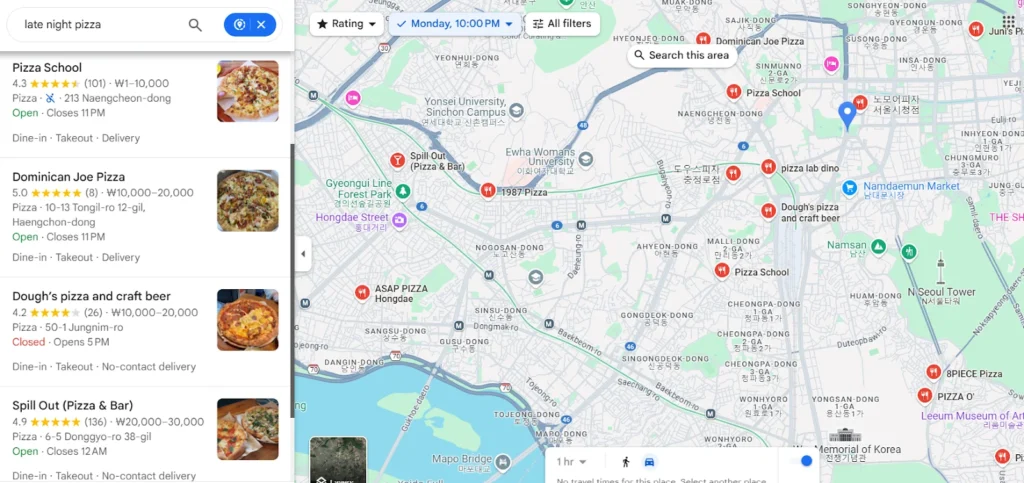
Local search ads combine keyword targeting with geographic targeting to connect businesses with high-intent users actively looking for nearby solutions.
Mobile App-Based Geo Ads
These ads are served within mobile apps that have access to a user’s location data. Ad networks and app developers integrate SDKs that allow advertisers to serve location-specific promotions within games, weather apps, or news platforms.

For example, a fitness club might deliver a limited-time joining offer to users using a health-tracking app within a 3-mile radius of the facility. These ads often support rich media formats such as video or interstitials to improve engagement.
They provide an opportunity to reach users in a highly personalized, mobile-first environment, especially effective when paired with contextual app behavior data.
Social Media Geo Ads
Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, Snapchat, and TikTok offer geo-targeting capabilities that let advertisers segment audiences by city, postal code, radius, or location clusters. These ads appear in users’ feeds, stories, or reels, depending on the format.
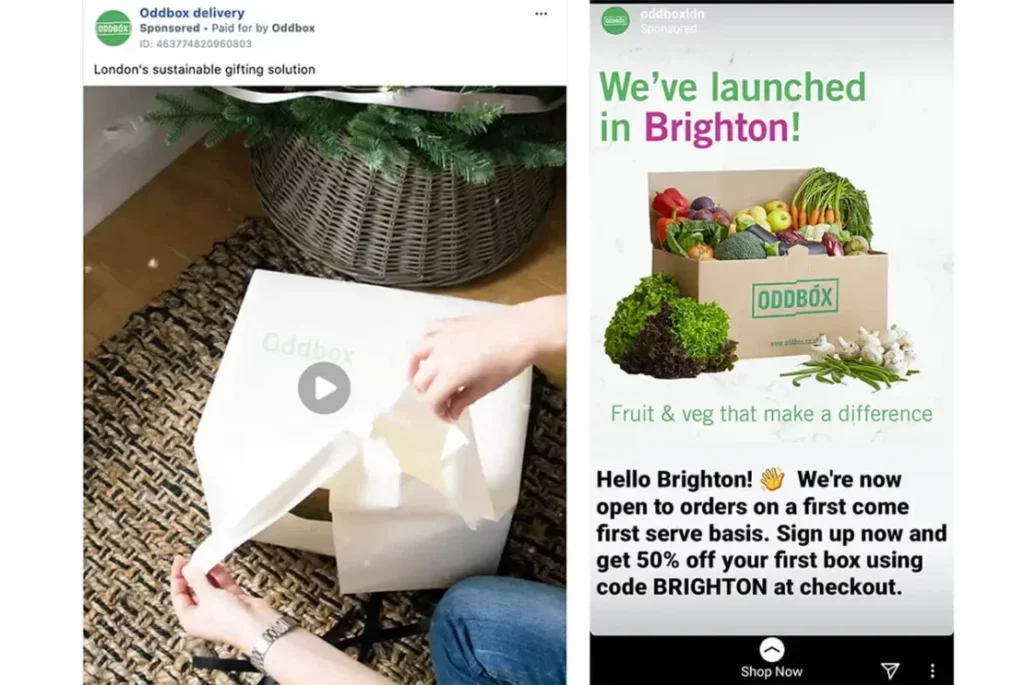
An event venue might run Instagram Story ads promoting a local concert only to users located within a 10-mile radius of the venue. Facebook Ads Manager also allows for layering location with behavioral and interest-based targeting to refine delivery even further.
Social geo ads are effective due to their native format, real-time delivery, and strong visual storytelling potential. They are ideal for raising awareness and driving foot traffic quickly.
Programmatic Local Display Ads
Programmatic local display ads use automated ad buying systems to serve display banners to users in specific locations across a vast network of publisher websites and mobile apps. These campaigns leverage real-time bidding (RTB) and data-driven targeting for precision delivery.
A local insurance agency could run programmatic banner ads targeting users within a specific ZIP code who have recently searched for auto coverage. These ads can adapt messaging dynamically based on time of day, weather, or location triggers.
This method excels at scale, delivering broad reach while maintaining localized messaging. It’s well-suited for sustained brand visibility and remarketing across various platforms.
Setting Up a Geo-Targeted Campaign (Step-by-Step)
Geo-targeted ad campaigns require more than just setting a location filter. Their effectiveness lies in their precision, reaching users when and where they are most likely to convert. Here’s a breakdown of how to set one up.
- Define the Business Goal and Conversion Metric: Clarify the intended action before selecting a location or platform. The campaign’s setup depends on this clarity, whether it’s increasing in-store visits, calls, or local event attendance.
- Choose the Right Advertising Platform: Select a platform that aligns with your audience’s behavior. Google Ads is ideal for intent-based searches, while Facebook and Instagram excel at community-based engagement.
- Narrow the Geographic Scope: Specify the target area using options like radius targeting (e.g., 5 km from store), ZIP codes, or custom map boundaries. Be as specific as possible to avoid wasting impressions.
- Define the Audience: Combine geographic filters with behavioral or demographic targeting. For example, target users aged 25–45 within a 10 km radius who have shown recent interest in fitness products.
Best Facebook Ads Targeting Strategy for 2025
- Craft Ad Creatives That Reference the Local Context: Mention local landmarks, neighborhood names, or time-sensitive local offers to resonate more deeply.

Example: Seahawk Deal Advertisement by Skittles During Super Bowl 2014 in Seattle
- Set Appropriate Bidding Strategies and Budget: Use automated bidding (like Target ROAS or Maximize Conversions) and allocate budget based on population density and competition in each zone.
- Monitor and Iterate: Measure performance using platform analytics and footfall tracking tools. Adjust based on which locations are driving ROI and which are underperforming.
Best Platforms for Running Local Geo-Targeted Ads
Not all platforms are equally effective for every type of local campaign. Depending on the objective, audience behavior, and location data quality, some platforms offer stronger geo-targeting capabilities than others.
- Google Ads: Ideal for capturing high-intent “near me” search traffic. Google allows radius targeting around physical addresses and location extensions for better visibility.
- Meta Ads (Facebook and Instagram): Strong for demographic layering and community engagement. Meta allows real-time targeting based on current user location, interests, and local event relevance.
- Waze Ads: Useful for driving physical foot traffic. Waze offers branded pins and takeover ads when users approach a business location, which is ideal for retail and food service.
- Snapchat Ads: Geofilters and location lenses allow real-time, immersive local campaigns, especially relevant for event-based and Gen Z targeting.
- Yelp Ads: Focuses on consumer intent and local discovery. Particularly useful for restaurants, salons, and local services, where reviews and visibility play a major role.
Each of these platforms has unique strengths in location accuracy, ad formats, and user engagement. Hence, platform selection should align with campaign goals and audience intent.
Best Practices for High-Performance Geo Ads
Geo-targeted campaigns perform best when they are localized, time-sensitive, and tied directly to in-store outcomes. Implementing nuanced practices can significantly improve engagement and conversion rates.
Use Local Language and Time-Specific Offers
Incorporate locally familiar terms, neighborhood names, or regional phrases into ad copy to build relatability. Time-specific offers, like “Lunchtime Specials Until 2 PM,” drive urgency and capture real-time intent.
Land O’Lakes, Inc.: Tulare Is Incredible
Example: Land O’Lakes Showcasing California’s Dairy Community in Their Ad
Sync Online Campaigns with In-Store Promotions
Ensure that digital messaging aligns precisely with what customers will see or experience on-site. A disconnect between advertised offers and in-store promotions can erode trust and reduce repeat visits.
A/B Test Locations and Radii
Not all proximity zones yield the same ROI. Run split tests on different radii (e.g., 1 km vs. 5 km) and locations (urban core vs. suburb) to identify the most responsive zones.
Optimize for Mobile and Map-Based Visibility
Most local-intent actions stem from mobile users navigating maps or local listings. Prioritize ad formats like Google Local Inventory Ads, clickable call extensions, and Waze-branded pins that cater to mobile-first behaviors.
Success in geo-ads hinges on seamless integration between messaging, physical location data, and mobile responsiveness. Without alignment across these touchpoints, even well-funded campaigns can underperform.
Mistakes to Avoid in Geo-Targeted Advertising
Despite its precision, geo-targeting can backfire when mismanaged. Below are common pitfalls that undermine campaign performance and inflate costs.
- Over-Narrow Targeting: Limiting ads to a highly tight radius may exclude potential customers who are nearby but not within the defined range. A more strategic approach is layering targeting with behavioral data.
- Ignoring Ad Scheduling Based on Local Footfall: Serving ads during low-traffic hours wastes budget. Use insights from foot traffic analytics or store POS data to align ad delivery with peak local activity periods.
- Not Aligning Ad Messaging with Physical Store Experience: If the ad promotes a specific product, but that product is out of stock or unavailable in-store, customer frustration increases. Ensure inventory, offers, and messaging are synced.
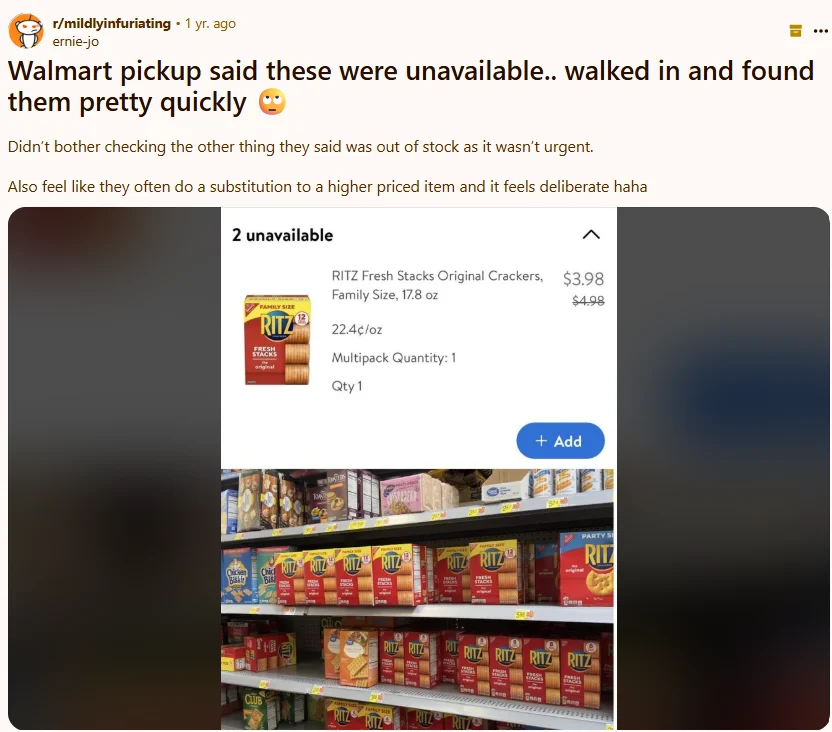
Example
- Inadequate Location Tracking in Analytics: Without enabling proper tracking (e.g., Google Ads location reports or UTM parameters), it’s challenging to attribute in-store visits or conversions to digital campaigns, reducing the clarity of ROI.
Each of these mistakes showcases friction between ad engagement and real-world results. Eliminating them requires both strategic planning and operational coordination between digital and physical touchpoints.
Case Studies: Local Businesses That Grew with Geo Ads
Geo-targeted advertising has proven effective for various businesses aiming to increase local engagement and foot traffic. Below are three real-life examples illustrating successful strategies and outcomes.
McDonald’s: Enhancing In-App Engagement with Geofenced Billboards
McDonald’s collaborated with Waze to integrate geofenced billboards with in-app advertising.
When drivers approached these billboards and came to a complete stop, a full-screen “Zero Speed Takeover” ad appeared on their mobile devices, prompting them to navigate to the nearest McDonald’s location.
This campaign resulted in 6.4 million mobile impressions and 8,400 in-app actions, demonstrating the effectiveness of combining out-of-home advertising with mobile engagement.
Starbucks: Utilizing Geofencing for Timely Promotions
Starbucks employed geofencing technology to send push notifications to customers’ mobile devices when they were near a Starbucks location.
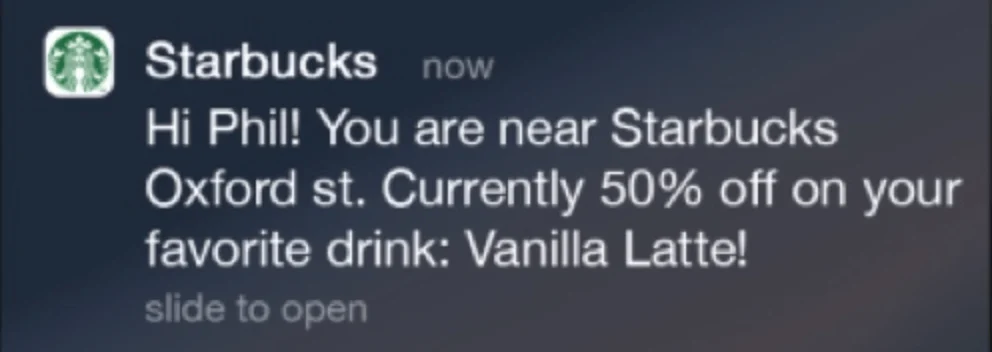
These notifications often promoted time-sensitive deals, such as their “Happy Hour” specials, encouraging immediate visits.
This strategy effectively increased foot traffic during targeted times by reaching customers at moments when they were most likely to make a purchase.
Coca-Cola Consolidated: Gathering Local Insights Through Geo-Targeted Panels
Before launching television ads in key local markets, Coca-Cola Consolidated used 1Q’s geo-targeting and demographic software to conduct customer panels.
This approach allowed them to gather immediate feedback from specific regions, ensuring that their advertising resonated with local audiences. The insights gained guided their marketing investments and enhanced the effectiveness of their campaigns.
Conclusion
Geo-targeted advertising enables businesses to connect with local audiences effectively, driving engagement and increasing foot traffic.
Implementing geo-targeted strategies can enhance marketing efforts, ensuring that promotional content reaches the most relevant audience segments.