The modern internet runs on search engines. Whether you’re conducting research, finding products, or optimizing your content for visibility, the choice of search engine can make a significant impact.
While Google dominates much of the global market, it is far from the only viable option. Different engines prioritize different needs: privacy, speed, regional results, academic indexing, or alternative content types.
This guide will offer a deep dive into the top 17 search engines currently shaping the digital landscape. Each one is evaluated not only by popularity but also by functionality, strengths, and where it fits in a business context.
Whether your goal is better SEO, safer browsing, or sourcing high-quality content, this comprehensive breakdown will help you navigate which search engine truly fits your needs.
Table of Contents
What Makes a Search Engine “Best”?
Search engines are not one-size-fits-all. The definition of “best” depends heavily on user goals and context. Below are the key criteria used in our rankings.
- Relevance: How accurately the engine returns meaningful and up-to-date results.
- Privacy: How well the engine protects user data, avoids tracking, and prevents fingerprinting.
- Speed: The average load time for query results and a seamless browsing experience.
- Features: Extra tools like image search, filters, preview panels, and AI summarization.
- Market Share: Current global user base, influence, and adoption in different industries.
- Localization: Ability to serve region-specific, language-specific, or culturally relevant results.
Search quality isn’t always synonymous with user experience. Some privacy-focused engines offer fewer features but appeal to security-conscious users. Others, like Google, provide robust tools at the cost of user data collection.
Different use cases demand different engines:
- SEO Research: Engines with large datasets and rich SERP features like Google and Bing.
- Privacy Protection: DuckDuckGo, Startpage, and Brave Search focus on zero-tracking environments.
- Academic and Technical Research: Semantic Scholar, Google Scholar, and Wolfram Alpha cater to precision and source reliability.
- Multilingual or Regional Queries: Yandex, Baidu, and Naver dominate in specific languages and countries.
Choosing the best engine requires balancing performance, data policies, and task-specific needs. The following section will break down each major engine to help identify which is most suitable for your operational or strategic goals.
The Top 17 Search Engines in the World
Let’s right get into the list-
Google remains the undisputed leader in the global search engine market, with over 90% market share across most regions.
Its dominance is attributed to unparalleled algorithmic relevance, rich SERP features, and constant innovation through AI integrations like Search Generative Experience.
Key Features
- AI-enhanced results with contextual awareness
- Localized search and maps integration
- Rich snippets, image/video packs, and People Also Ask boxes
- Google Lens, Shopping, and News verticals
- Google Trends and Search Console for SEO data
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Most comprehensive index of websites | Data collection and tracking |
| Best-in-class tools for advertisers and marketers | Can prioritize ads over organic results |
| Superior user interface and experience | Personalized results may create filter bubbles |
| Frequent algorithm updates ensure relevancy | SEO can be volatile due to algorithm shifts |
Google is ideal for advertisers, content creators, and businesses optimizing for mainstream visibility. However, privacy-conscious users or those seeking niche or unbiased results may prefer alternatives.
Bing
Bing is Microsoft’s search engine, offering solid competition with its integration into Windows, Edge, and now ChatGPT-powered Copilot. While it holds a smaller market share than Google, Bing’s features have grown steadily in relevance and depth.
Key Features
- Built-in AI assistant via Copilot
- Enhanced visual search capabilities
- Cashback and rewards for search usage
- Microsoft Advertising platform
- Deep indexing of academic and shopping content
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Strong performance in image and video searches | Smaller index compared to Google |
| Privacy settings stronger than Google’s defaults | Some search results feel outdated or redundant |
| Integrates with the Windows ecosystem | Limited global reach in non-English regions |
| Competitive ad pricing for PPC campaigns | Fewer rich features in some verticals |
Bing suits budget-conscious advertisers, Edge users, and those looking for an AI-integrated search experience. It’s also a valuable secondary engine for cross-checking results in competitive analysis.
Yahoo Search
Yahoo Search is powered by Bing’s infrastructure but maintains its own user interface, news integrations, and brand recognition, especially in the U.S. and Japan.
Despite its diminished market share, it remains relevant for legacy users and offers business integration potential through Yahoo-Japan’s unique properties.
Key Features
- Bing-powered results with Yahoo interface enhancements
- Direct integration with Yahoo Finance, Sports, and News
- Personalized homepage and content recommendations
- Email and calendar ecosystem tie-in
- Regional strength in Japan via Yahoo Japan (operated independently)
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Familiar UI for older users and long-time Yahoo customers | Dependent on Bing’s indexing and algorithms |
| Unique ad opportunities through Yahoo Gemini | Limited innovation and feature development |
| Popular in Japan with region-specific integrations | Not a privacy-focused engine |
| Multi-vertical content from the Yahoo ecosystem | Search results may lag behind Google in freshness |
Yahoo Search can be a worthwhile traffic source for advertisers targeting Yahoo loyalists or audiences in Japan. However, it holds a slight advantage in terms of innovation or technical SEO.
Baidu
Baidu is the dominant search engine in China, with over 70% market share. It is tailored to Mandarin-language users and heavily localized. From AI and maps to medical information and business directories, Baidu functions more like a portal than a simple search tool.
Key Features
- NLP-optimized results for Mandarin queries
- Integration with Baidu Maps, Baike (encyclopedia), and Zhidao (Q&A)
- Rich snippet format for local business and service listings
- Baidu Webmaster Tools and mobile-friendly indexing
- Strong AI initiatives via Ernie Bot and content recommendation systems
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Essential for Chinese market visibility | Strict government censorship and content filtering |
| Built for the Chinese language and regional nuance | Not ideal for non-Mandarin websites |
| Comprehensive app ecosystem across multiple sectors | Complex verification process for site indexing |
| Fast, mobile-optimized experience in China | SEO practices differ significantly from global norms |
Baidu is indispensable for brands targeting mainland China. Localization, regulatory compliance, and Mandarin-language optimization are crucial for success on this platform.
Yandex
Yandex is the leading search engine in Russia and retains a strong influence in Eastern Europe. It offers a broad suite of services (mail, navigation, cloud, and translation), while its search engine is tuned to the complexities of the Russian language.

Key Features
- The algorithm is adapted to Russian morphology and synonyms
- Advanced filters and tools for images, videos, and maps
- Yandex.Metrica for deep traffic and behavior analytics
- Built-in advertising platform: Yandex.Direct
- Vertical search for goods, transport, weather, and news
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Superior accuracy for Cyrillic and Russian-language searches | Limited adoption outside Russia and ex-Soviet states |
| Metrica is more detailed than Google Analytics in many ways | Political tensions may limit global use |
| Deep integration with local services and infrastructure | Slower indexing for English-language content |
| Solid ad network for Eastern European outreach | Privacy policies may not meet Western standards |
Yandex is essential for businesses targeting Russian-speaking users. However, it is less suitable for general global search visibility or privacy-sensitive operations.
DuckDuckGo
DuckDuckGo is widely recognized as the go-to privacy-focused search engine. It doesn’t track users or store personal information and aggregates results from over 400 sources, including Bing, Yahoo, and its own crawler, DuckDuckBot.
It appeals to users looking to browse anonymously without sacrificing functionality.
Key Features
- No user tracking or search history storage
- Bangs feature for instant site-specific queries
- Based on a hybrid model of web crawling and external APIs
- Clean, minimal interface with instant answer
- Available via browser extension and mobile app
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Excellent for users seeking anonymity | Lacks personalized search refinement |
| Supports over 1,000 site shortcuts via !bangs | Heavy reliance on Bing for core results |
| Transparent privacy policy and open-source elements | Not ideal for localized or ultra-niche content |
| Avoids filter bubbles in search rankings | Its ad revenue model still ties back to search partner networks |
DuckDuckGo is a preferred option for privacy-conscious users and brands aiming to associate with ethical tech. However, it’s not the best choice for businesses relying on user-specific targeting or personalization.
Ecosia
Ecosia is an eco-friendly search engine that donates 80% of its profits to reforestation projects. While its results are powered by Bing, the platform has carved out a niche among environmentally conscious users.
Ecosia also maintains transparency by publishing monthly financial reports and tree-planting receipts.
Key Features
- Tree planting funded by ad revenue
- Transparent financial reporting and environmental impact data
- Uses Bing for search results and image data
- Chrome, Firefox, and mobile integration
- Carbon-neutral infrastructure with green energy servers
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Strong environmental branding and appeal | Search quality is limited to Bing’s data |
| Clear, quantifiable mission impact | Lacks advanced features or toolsets for power users |
| Ethical and privacy-friendly business model | No original indexing or custom search engine technology |
| Appeals to eco-aware demographics | Smaller market share and visibility |
Ecosia is ideal for businesses or individuals aligning their operations with sustainability values. While not technically innovative, it excels in brand positioning and cause-driven engagement.
Brave Search
Brave Search is a privacy-respecting search engine developed by the makers of the Brave browser. Unlike DuckDuckGo, it uses its own independent index, which gives it more control over rankings and less dependency on third parties.
It is in active development and aims to be a full-featured alternative to Google and Bing.

Key Features
- Fully independent index (no reliance on Bing or Google)
- Privacy-first architecture with zero tracking
- Available natively within the Brave browser
- Goggles feature for customizable ranking models
- Open to community curation and transparency feedback
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Offers original indexing with growing independence | Still developing in terms of depth and scale |
| Ideal for privacy-focused professionals | May lack completeness in niche topics |
| Supports Web3 and decentralized internet concepts | Some instability with experimental features |
| Active roadmap and responsive to community needs | Lower market penetration compared to DuckDuckGo |
Brave Search is best suited for early adopters, Web3 supporters, and businesses focused on digital ethics and decentralization. It’s still maturing but promising in terms of independence and innovation.
Startpage
Startpage is a Netherlands-based search engine that offers the privacy benefits of DuckDuckGo but with Google-powered search results. It acts as a proxy, fetching Google results on behalf of the user without storing IP addresses, search history, or using trackers.

Key Features
- Google’s search index with full user anonymity
- Anonymous View proxy feature for private website browsing
- No logging of personal information or search behavior
- European data protection compliance (GDPR)
- Clean, familiar UI and ad-free experience with the paid version
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Combines Google-quality results with zero tracking | Limited customization or personalization options |
| Fully GDPR-compliant and based in privacy-forward jurisdictions | Slower response time due to proxy relaying |
| Allows anonymous browsing of target websites | No rich features like image tools or shopping results |
| Ideal for journalists, researchers, and legal professionals | Does not support deep integrations or local results accuracy |
Startpage is best suited for professionals who need Google’s comprehensive search capabilities but cannot risk data exposure. It balances privacy and performance better than most intermediaries.
Qwant
Qwant is a France-based search engine developed with a strong commitment to user privacy and European digital sovereignty.
It uses its own indexing technology for most queries and supplements with Bing when necessary. Qwant’s interface includes dedicated verticals for music, news, and social media.

Key Features
- Own search index supplemented by Bing
- No tracking, profiling, or cookies
- Compliant with EU data protection laws
- Categorized search portals (Web, News, Social, Music, Images)
- Designed for schools and public sectors via Qwant Junior
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Emphasizes European data privacy and independence | Index depth is not as extensive as Google or Bing |
| Offers curated experiences for education and public use | Results can sometimes be outdated or less relevant |
| Visually organized interface with topic separation | Lacks global adoption and multilingual optimization |
| Suitable for public institutions with compliance needs | Occasional performance lag during high-traffic periods |
Qwant is ideal for European businesses, institutions, or developers needing privacy-first alternatives with regional compliance. It’s also effective for those seeking structured content navigation across verticals.
Swisscows
Swisscows is a privacy-focused, family-safe search engine based in Switzerland. It uses semantic search technology to understand intent and context, rather than keyword matching alone.
It does not store user data or use tracking technologies, and its data centers run entirely on renewable energy.

Key Features
- Semantic search engine with AI-enhanced intent recognition
- No tracking, cookies, or search history collection
- Physically located in Switzerland with strong privacy laws
- Integrated family-friendly filter by default
- Operates on 100% renewable energy
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Strong privacy backed by Swiss legal framework | Semantic engine is still limited in complex queries |
| Built-in family-safe filters, ideal for educational use | Not suitable for adult, niche, or technical content |
| Green infrastructure and ethical branding | Search depth can’t match major competitors |
| Great for users valuing ethical, secure digital environments | Runs on a subscription model only (as of the time of writing) |
Swisscows is a solid choice for education providers, ethical brands, and families. It aligns well with clean tech, privacy assurance, and semantic AI, though it may fall short for technical professionals or global commerce needs.
You.com
You.com is a relatively new search engine that merges traditional web results with AI-powered apps. It offers a customizable, productivity-oriented interface, along with features like code search, AI chat, and real-time summarization.
You.com operates its own index and aims to be a search assistant rather than just a search engine.
Key Features
- Modular, app-based search results from diverse sources
- Built-in AI tools for summarizing, writing, coding, and chatting
- Supports incognito private search with no tracking
- Customizable interface with “thumbs up/down” ranking
- Developer-friendly options and integrations for productivity
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Combines AI and search in a single platform | Index is still developing compared to giants like Google |
| Powerful for research, coding, and writing tasks | May overwhelm users who prefer traditional formats |
| Transparent about data handling and privacy options | Some features are gated behind its freemium model |
| Customizable output improves workflow efficiency | AI summaries may introduce factual inaccuracies |
You.com is ideal for developers, researchers, or entrepreneurs who value speed, multitasking, and AI-assisted decision-making over a conventional browsing experience.
Dogpile
Dogpile is a metasearch engine that aggregates results from several mainstream sources, including Google, Bing, Yahoo, and Yandex. While its interface is dated, it remains a useful fallback for users who want an overview across search providers.
Key Features
- Combines results from major search engines
- Simple, old-school interface with minimal ads
- Separate tabs for images, videos, news, and shopping
- Quick-access filters for recent queries and categories
- No account required or persistent tracking
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Multi-engine aggregation increases the diversity of results | Results often include redundancy or ads from multiple sources |
| No user tracking or profiles needed | The interface lacks modern polish or responsiveness |
| Useful for comparative research across engines | Relevance may suffer due to a lack of personalization |
| Accessible for quick generic lookups | Not suitable for complex or niche search needs |
Dogpile is best suited for casual users or researchers who want to sample multiple engines without toggling tabs. It’s also a handy alternative for quickly checking ranking parity.
Mojeek
Mojeek is a fully independent crawler-based search engine built in the UK. It doesn’t rely on Bing or Google APIs and is notable for indexing and ranking content with zero tracking. Mojeek positions itself as the rare example of an autonomous search engine with ethical data principles.
Key Features
- Independent web crawler and index
- No use of tracking cookies or user profiling
- Hosted in UK-based green data centers
- Textual relevance scoring without commercial bias
- Real-time transparency logs for indexing
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Total independence from other search providers | Its smaller index results in a lower breadth of content |
| Committed to zero-tracking, privacy-first operation | Search relevancy and depth are not yet competitive |
| Ethical alignment with green computing and transparency | Limited international language and localization support |
| Ideal for ethically conscious and minimalists | No advanced features like news clustering or AI snippets |
Mojeek is recommended for ethical businesses, researchers, and individuals, prioritizing autonomy, environmental sustainability, and long-term data privacy over market-driven ranking.
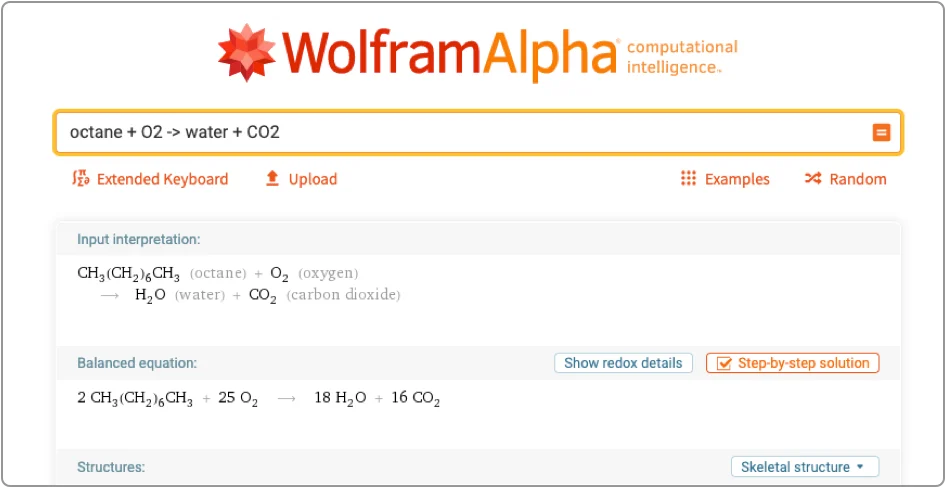
Wolfram Alpha
Wolfram Alpha is a computational knowledge engine. Rather than returning web pages, it computes factual answers from curated data, algorithms, and structured knowledge across science, math, engineering, finance, and more.

Key Features
- Computes answers rather than fetching websites
- Covers scientific, mathematical, statistical, and financial domains
- Step-by-step problem solving for complex equations
- Data-driven visualizations and charts
- Pro version includes file uploads, custom queries, and extended computation
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Ideal for factual, analytical, and scientific inquiries | Not designed for browsing or content discovery |
| High reliability in structured domains like physics, finance, and math | Lacks coverage in subjective or content-rich topics |
| Visual and dynamic output with instant graphs and formulas | No support for media or traditional link-based search |
| Strong educational and professional utility | Requires the premium plan for advanced usage scenarios |
Wolfram Alpha is ideal for students, data analysts, engineers, and educators needing calculated, real-time answers without sifting through search results.
Presearch
Presearch is a decentralized, blockchain-based search engine that rewards users with cryptocurrency for using the platform. It emphasizes privacy, community governance, and Web3 integration, appealing to tech-savvy users and alternative internet proponents.
Key Features
- Uses multiple engines through custom node routing
- No tracking or personal data collection
- Offers PRE crypto tokens as incentives
- Transparent, community-driven infrastructure
- Open ecosystem for developing custom search nodes
| Strengths | Limitations |
| High user privacy with decentralized infrastructure | Still in the development phase compared to mature platforms |
| Token-based incentive model encourages engagement | Search relevance may vary based on node behavior |
| Customizable experience with third-party integrations | Lacks deep indexing capabilities of centralized engines |
| Appeals to Web3 and open-internet enthusiasts | Requires some crypto literacy for optimal use |
Presearch is ideal for privacy advocates, blockchain enthusiasts, and businesses exploring Web3 interoperability and alternative ecosystems outside mainstream tech giants.
Wayback Machine
The Wayback Machine, created by the Internet Archive, functions less like a traditional search engine and more like a time capsule of the web.
It allows users to access snapshots of websites across different periods, making it invaluable for research, digital forensics, and historical referencing.
Key Features
- Access archived versions of websites dating back to 1996
- Includes over 800 billion web pages
- Useful for recovering lost or deleted content
- Supports historical SEO audits and digital compliance
- Free to use and maintained by a nonprofit organization
| Strengths | Limitations |
| Massive archive of the historical web | Not ideal for real-time or transactional queries |
| Supports digital research, legal evidence, and brand history tracking | Search functionality within the archive is limited |
| Excellent for content recovery and backlink verification | Some websites are excluded due to robots.txt restrictions |
| Maintains digital transparency and open access | Interface and load speed can be clunky |
The Wayback Machine is a powerful research tool for legal teams, digital marketers, journalists, and historians seeking to verify, audit, or preserve web content.
Comparison Table: Key Metrics at a Glance
Here’s a comparative breakdown across essential technical and user-experience criteria to give a holistic view of these 17 search engines.
Each engine brings unique strengths, and this table helps clarify where each stands relative to others in areas like privacy, ad policies, and data scope.
| Search Engine | Market Share | Privacy Rating | Index Size | Ad Intrusiveness | Region Popularity | Open Source/Proprietary |
| ~91% (global) | Low | Extremely Large | High | Global | Proprietary | |
| Bing | ~3% (global) | Medium | Very Large | High | US, UK, Canada | Proprietary |
| Yahoo Search | ~1.2% | Low-Medium | Large (via Bing) | High | Japan, US | Proprietary |
| Baidu | ~1% (global) | Low | Very Large | High | China | Proprietary |
| Yandex | ~0.5% | Low-Medium | Large | Medium | Russia, CIS | Proprietary |
| DuckDuckGo | ~0.6% | High | Medium (uses APIs) | Low | US, Europe | Proprietary |
| Ecosia | ~0.1% | High | Medium (via Bing) | Low | Germany, Europe | Proprietary |
| Brave Search | Growing | Very High | Medium-Large | Very Low | US, UK | Partially Open Source |
| Startpage | Niche | Very High | Medium (via Google) | Very Low | Europe | Proprietary |
| Qwant | Niche (EU-based) | High | Medium | Low | France, EU | Proprietary |
| Swisscows | Niche | Very High | Small-Medium | Very Low | Switzerland, Germany | Proprietary |
| You.com | Niche | High | Medium | Low | US, tech-savvy users | Partially Open Source |
| Dogpile | Very Low | Low | Aggregator | High | US (legacy audience) | Proprietary |
| Mojeek | Very Low | Very High | Medium | Very Low | UK, Privacy-first users | Fully Open Source |
| Wolfram Alpha | Niche | Medium | Specialized | None | Global (academia, STEM) | Proprietary |
| Presearch | Very Low | Very High | Medium (via nodes) | None | Crypto/Web3 communities | Decentralized/Open |
| Wayback Machine | Niche (archive) | High | Massive Archive | None | Global (research) | Open Source (Archive.org) |
Niche Search Engines Worth Mentioning
While mainstream engines serve general needs, several niche search engines offer unique value for research, academic exploration, and specialized queries. These platforms may not compete on traffic volume but excel in precision, privacy, or community-specific indexing.
- Internet Archive Search: This is the search interface for the Internet Archive, which includes digitized books, audio, video, websites, and scholarly materials.
Ideal for academic and historical referencing, it provides access to content rarely indexed by standard engines.
- Semantic Scholar: Designed for scientific literature, Semantic Scholar indexes millions of research papers and leverages AI to extract key insights. It’s particularly strong in computer science, medicine, and neuroscience.
- Boardreader: This search engine focuses on forums, message boards, and community discussions.
Business owners can use it to monitor niche communities, identify sentiment trends, or research competitor mentions across platforms like Reddit and old-style forums.
- Marginalia Search: A privacy-first search engine indexing small websites, blogs, and independent thinkers. Its goal is to resurface the non-commercial internet, making it valuable for curated research and low-noise data discovery.
- Wolfram Alpha Pro: While Wolfram Alpha is already on the main list, its Pro version deserves separate mention for businesses and researchers who rely on computational data analysis, structured outputs, and API-driven integrations.
How to Choose the Right Search Engine for Your Needs
Choosing the optimal search engine isn’t about popularity alone. Depending on industry, goals, and data sensitivity, the “best” tool varies significantly. Here’s how to decide:
- For General Business Use and SEO Monitoring: Use engines with high market share and reliable indexing like Google, Bing, or Yahoo. They’re essential for visibility analysis and keyword performance monitoring.
- For Privacy-Conscious Browsing: Engines like DuckDuckGo, Startpage, and Mojeek offer strong privacy standards without tracking or personalized profiling, making them ideal for confidential research.
- For Global vs. Regional Markets: Baidu dominates in China; Yandex serves Russia and CIS countries. For EU markets, Qwant and Swisscows align better with GDPR-conscious audiences.
- For Scientific and Academic Research: Semantic Scholar, Wolfram Alpha, and Internet Archive Search offer structured data and peer-reviewed content unavailable on commercial engines.
- For Monitoring Forums and Niche Communities: Boardreader and You.com are good picks for businesses tracking user sentiment in discussion-based content across multiple platforms.
- For AI-Powered Summaries or Vertical Search: Brave Search, You.com, and Presearch offer unique verticals like code, news, or science, and increasingly rely on AI for summarization or context generation.
Future of Search Engines: Trends to Watch
The future of search is rapidly shifting toward decentralized systems, AI-driven query understanding, and user-controlled data.
The era of simple keyword matching is evolving into intent prediction powered by machine learning models that can understand nuance, context, and content format preferences.
AI summarization will likely become mainstream, as seen in Brave Search and You.com, reducing the need to click through multiple links.
In parallel, open-source indexing (represented by Mojeek and Presearch) is gaining traction for its transparency and resistance to commercial manipulation.
Vertical search engines focusing on domains like academic papers, legal content, or forums are also set to expand. These engines deliver cleaner datasets for specific business workflows and reduce the noise of commercial content.
Additionally, privacy legislation like GDPR and CCPA is influencing architecture decisions. Expect more engines to embrace anonymized browsing, encrypted queries, and on-device personalization.
Finally, voice and visual search will grow as generative AI systems continue to merge search intent with real-time content generation, potentially redefining how information is accessed altogether.
Conclusion
Choosing the best search engine is about identifying the one that meets specific needs, whether for SEO, privacy, research, or region-specific marketing.
Every engine has a purpose, from global giants like Google and Bing to niche options like Mojeek and Semantic Scholar.
In a data-saturated world, the right search engine is a strategic advantage.